What is a Variable Frequency Drive?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is a power transformer used to control the rotational speed of an engine acting on the power frequency. This system is powered by a direct current (DC) voltage which it changes to alternating current (AC) voltage.
» Electronic circuit inverter
» Transforms direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC)
» Controls engine speed
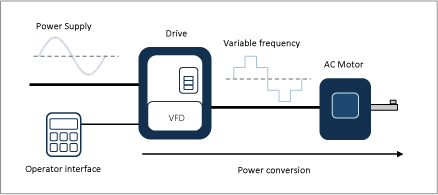
The speed of these engines depends on the frequency applied, as well as on the wound pattern and to a lesser extent on the load. Therefore, in order to meet the speed of an induction engine, it is necessary to control the frequency of the power supply. In addition, it must be borne in mind that in order to examine the speed of an AC induction engine, a more complex controller called a Frequency Converter or Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is required..
The engines with variable frequency drives allow a wide variety of applications since they reduce energy consumption and prolong the operational life of the engines to which they are applied thanks to their more effective starting. Control is achieved by varying the frequency applied to the engine.
The use of the appropriate cable
The large number of harmonics generated by the drive output pulses produce high frequency induced surges that cause current circulation inside the engine due to mismatch impedance between the power supply cable and the engine, causing erosion in engine components. In order to extend the operational life of the engine, this aspect must be taken into account and the necessary means considered in order to mitigate the problem as far as possible from installation design.
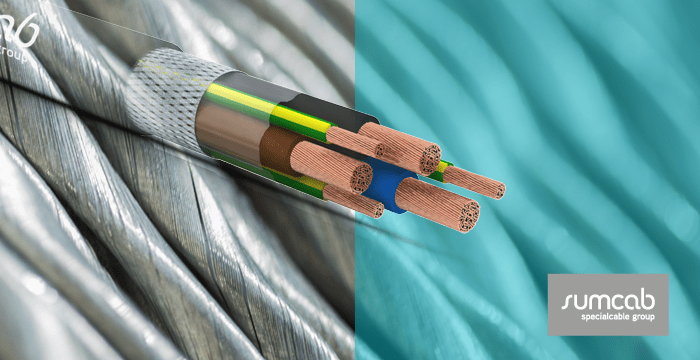
Cable with symmetrical design
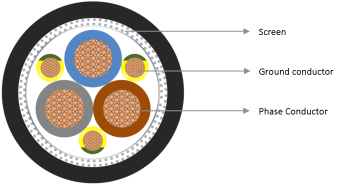
The VFD cable design consists of concentric cables of 4 conductors or symmetrical earth cables distributed between the interstices generated when isolated phases coincide. This is how each interstice houses 1/3 of the total ground conductor cross-section area; achieving a physical and electrical symmetry in the cable. This uniformity guarantees a more balanced ground system.
The screen is responsible for preventing the dissipation or release of the noise created by the energized cable and, in turn, preventing the entry of the external noise of the system.
SUMCAB
Expect High Performance