Not all work environments are the same. Some installations have specific requirements that need to be met with specific cable designs and characteristics.
What are ATEX Zones?
Atex zones are those with a high concentration of gases or dust that could potentially lead to a violent, fiery or dangerous explosion.
In fact, the letters refer to the abbreviation of “ATmosphère EXplosible”. Electrical wiring in such areas must therefore consider that risk of explosion or fire stemming from the presence of flammable substances.
The various situations that may arise within an ATEX zone can be defined according to a number of different characteristics. As a result, ATEX cables come in different categories and each ATEX zone should have a different type of cable installed to suit the characteristics in question.
The main distinction that is made when designing cables for ATEX zones relates to the specific risks that exist in each one.
We work with two categories:
- ATEX zones where gases, vapours and liquids are present fall into Category I.
- ATEX zones where dust is present fall into Category II.
ATEX cables for Category I zones
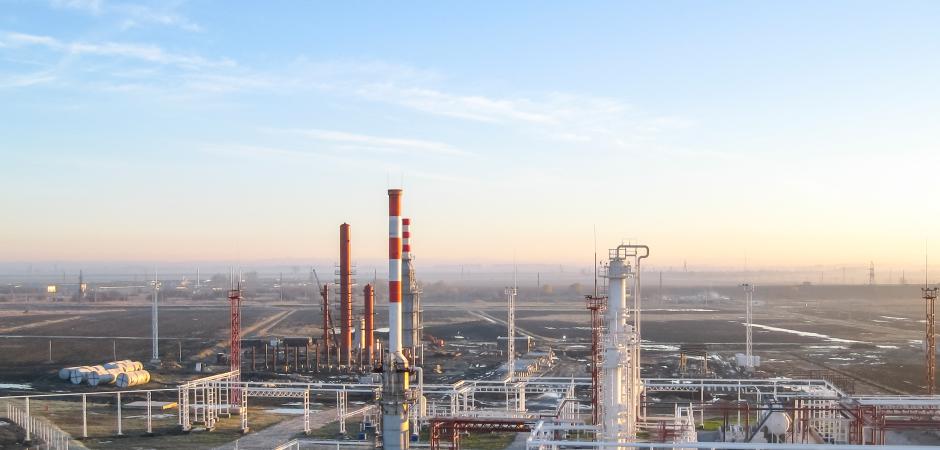
The installation of ATEX cables for Category I work environments mainly involves petrochemical plants, liquefied gas plants, combined-cycle power plants or refuelling stations.
Given that different concentrations of gases, vapours and liquids can be found in each of these locations, we have to design specific cables for the conditions of each one.
In order to meet the necessary safety requirements, the following distinction is made between the different Category I ATEX zones:
- Zone 0 - These hazardous materials are present in these areas either permanently, for a prolonged period of time or often.
- Zone 1 - There is a possibility of explosion in these areas under normal conditions.
- Zone 2 - It is not possible for these hazardous materials to exist in these areas under normal conditions or, if they do, they are only present for a brief period of time.
ATEX cables designed for a Category I zone will therefore need to deal with different gas, vapour and liquid concentrations depending on whether it is a Zone 0, Zone 1 or Zone 2. This distinction enables us to manufacture cables based on the conditions required in each area and to ensure they always maintain the highest levels of effectiveness.
Sumcab offers its PetroSumsave ATEX cables as the most suitable products for these working conditions.
ATEX xables for Category II zones
Category II ATEX zones are defined by their high dust concentrations at levels that could potentially pose a risk.
The industries in which these conditions arise include those engaged in the handling and storage of grain or by-products in the food industry, those engaged in the processing of wood such as timber workshops or saw mills, the paper industry or textile fibre processing and manufacturing plants, among others.
As is the case in Category I ATEX zones, a distinction is made between three different types of zone in category II based on the degree of dust concentration and the potential hazard it poses:
- Zone 20 - The concentration of dust exists either permanently, frequently or for a prolonged period of time.
- Zone 21 - Dust forms occasionally under normal operating conditions.
- Zone 22 - Dust forms infrequently and only persists for a short time if it does.
The most suitable cables for ATEX zones with these conditions can be found in the Sumsave range from Sumcab.
Characteristics of cables for ATEX zones
At Sumcab, we have a broad range of different cables for ATEX zones to meet the various conditions that exist in each one based on the level of danger that is present.
Nonetheless, generally speaking, all cables must have certain common characteristics or meet certain common requirements for these environments:
- ATEX cables must have an outer sheath made from heavy polychloroprene or a similar synthetic elastomer (PUR or TPE).
- In terms of strength, these cables must offer a similar level of performance to a rubber cable.
- The section containing the conductors must usually be at least 1 mm2.
- The cable mesh cannot be used as a protective conductor.
- The bending radius of the cable cannot exceed the ratios established by the manufacturer.
- Extrusion filled cables are recommended because they help to maintain a completely watertight connection.
Do you need ATEX cables that meet the needs of these environments? Get in touch with us for some personalised advice and, after studying the work environment.